| Mother & Child Care |
Pregnancy calendar
Pregnancy is a dream comes true. Nine months from now you will have a baby in your arms. It is an exciting time but full of curiosity. You will be eager to know how an unrecognizable mass of cells finally develops into a lovely full term baby.
We, at dhaliwal Hospital, have tried to make it easy for you to learn everything about your child’s development & growth. Our pregnancy calendar will accompany you on your journey to motherhood and help you in knowing the changes occurring to the precious life inside. The pregnancy calendar is a week by week description of events which take place from conception to delivery.
Week 1 & 2 Pregnancy is dated from the first day of your last period, which means for the first 2 weeks of pregnancy you are not actually pregnant.
Tip: - Take folic acid if you are planning to have a baby.
Discuss the emotional & financial implications with your partner.
Week 3 Fertilization could now be taking place
Week 4 You may miss your period
Week 5 Try a urine pregnancy test-> found it positive -> “congratulations”. See your doctor. Your breasts may start feeling tender. Heaviness or mild pain in lower abdomen like you get before periods may occur.
Week 6 The embryo if officially a fetus. The heart starts beating now and is visible on internal ultrasound.
Week 7 Avoid any medication without advice. This is important as the basic ‘structure’ of the body & all organs of the baby is formed in the first 12 weeks. You may also start feeling pregnant. Nausea, vomiting, mood swings & increased desire to urinate commonly occur.
Week 8 It’s not uncommon to feel tired even though you don’t look pregnant. The fetal limb buds, eyes & nervous system are developing rapidly.
Week 9 The fetus is 3.5-5cm long. Development of placenta begins. You may notice a slight thickening of your waistline. Don’t blame it on your tiny baby, it could be fluid retention
Week 10 The fetus starts making plenty of movements but you can’t feel anything for several weeks yet. You may gain a little weight. But if you haven’t don’t worry. Most of the weight gain occurs in the 2nd & 3rd trimester.
Week 11 The fetus looks like a small human now and is about the size of your little finger. Try eating frequent small meals & keep healthy snacks at your desk. You may be offered a scan between 11 & 14 weeks, especially if you are over 35, to measure the nuchal fold thickness which can screen for Down’s syndrome.
|
|
|
 |
| |
|
| |
 |
| |
|
| |
|
Week 12 The placenta is now well formed. The fetus is about 8 cms in length & 60 grams in weight. This is a period of emotional turmoil for you due to the increased hormonal levels. Nausea & vomiting starts to disappear.
Week 13 The facial features are starting to form. The uterus is now large enough & rises out of the pelvis to be felt per abdomen. Pregnancy is divided into 3 trimesters of 3 months each. You are reaching the end of your first trimester. See that all your routine investigations are complete.
Week 14 Your fetus has eyebrows, but no eyelashes. Fine light hair also begin to grow. Your arms, hip & face are beginning to look plumper.
Week 15 The cells which colour your baby’s hair begin to produce their colour now. Increase your fluid & fibre intake to prevent constipation. Skin pigmentation may start developing.
Week 16 By now, your baby has finger nails & toe nails, eyebrows & eyelashes. The hair that will cover your baby until the last week or so of pregnancy called lanugo starts to form. You will be visibly pregnant. Be proud of your bump.
Week 17 Your baby can hear sound from outside. You & your partner should talk to the baby. In mid pregnancy many women feel & look “blooming”
Week 18 Your baby is very active & you may actually feel the first “kick”. The placenta fully nourishes your baby & prevents a lot of infections. Your baby’s length is about 16 cms & weight is about 135 gms. You may have an ultrasound scan between 18-20 weeks to see if your baby is developing normally & there are no anomalies.
Week 19 By the end of this week your baby is about 20 cms long & weights 300gms. The babies teeth have formed in the gums. Eat plenty of fruits & vegetables.
Week 20 Your baby develops his own “waterproofing” system. A creamy- coloured greasy substance called vernix covers his body. You are halfway through your pregnancy. Movements can become active at this time. Start your antenatal exercise classes.
Week 21 Uterus increases in size & the baby moves vigorously. You may be able to see your baby move. You start developing stretches marks & get breathless on exertion.
Week 22 See if your baby has period of resting & moving. Babies sleep in the uterus & have some periods of intense activity in between. Watch your back. Bend from the knee, not from the waist.
Week 23 Your baby’s skeleton continues to develop & bones inside the skull begin to harden. Plan your maternity leave.
Week 24 Your baby is well formed & with most of his body parts in proportion but skinny. There is only a very small amount of fat laid down under the skin. Your baby is about 32 cms long & weights about 500 gms.
Week 25 Most of your baby’s vital organs are in place & formed & the remaining pregnancy is time for growth. However the lungs are still very immature. Your baby’s skin is very thin & translucent.
Week 26 Your baby’s skin is more opaque. Start playing music to your baby or sing when things are quiet.
Week 27 Your baby’s measures 34 cms & weight above 800 gms. Enjoy yourself as your baby grows.
Week 28 Your baby is about 35 cms & weights about 1 kg. Keep yourself well hydrated. Sugar testing is done between 26-28 weeks. You may have swelling of ankles of feet.
Week 29 Your baby’s growth requires you to keep up your energy levels. Don’t give into pregnancy cravings like pica.
Week 30 Your may notice the start of “practice” contractions, which don’t usually hurt from now on. Wear low heel shoes to prevent any injury
Week 31 Your baby is able to see in the uterus & knows when it’s light or dark. Your baby gets plumper as more fat is being deposited under the skin. You gain weight faster.
Week 32 Your baby is about 42 cms long & weights about 2 kg. A baby born now has a good chance of survival but will still need intensive help breathing & feeding. Wear loose, comfortable clothing.
Week 33 Your baby will begin to settle in a particular position. You may be uncomfortable at night. Try lying on your side with proper support.
Week 34 A baby born at this time has much better survival chances as lungs are usually mature by this time. Start packing your labour & birth bag. Try eating “little & often”.
Week 35 Keep up your exercise and walk and review your shopping list.
Week 36 If it is your 1st baby your baby’s head may engage in the pelvis any time now. You will have to pass urine more frequently.
Week 37 Your baby’s growing fast. Your baby’s lungs are fully mature now & breathing difficulties at birth would be most unlikely. You will be called weekly for antenatal checkups. Find time to relax & rest.
Week 38 Your baby can be born any time now. Be prepared. Check what your hospital expects you to bring in.
Week 39 Movements from your baby tends to slow down. There’s simply too little space. Your baby gets chubbier day by day. Your weight remains stable and you wait for labour to ensue.
Week 40 Your cervix will be preparing for the birth by softening –it’s actually called “ripening”. Any day your waters could break, labour pains could start or you could have show a loss of the mucus plug that keeps your cervix sealed.
“Congratulations! You have just given birth to a new life.”
Pre conception clinic
Optimizing the health of the mother before conception is important. Preconceptional counseling refers to prospective planning for a pregnancy prior to conception. Women are pre screened for health & risk potentials before attempting to be pregnant. Ideally, women should visit her gynaecologist around 3 to 6 months before actual attempts are made to conceive.
Although every women in childrearing years is a potential candidate, but women with nutritional deficiencies (folate, iron etc), medical disorders (diabetes, renal diseases etc), exposure to toxins require it the most to improve chances for a successful pregnancy. Preconceptional counseling is more important than antenatal care for prevention of congenital anomalies.
A detailed history is elicited from the woman regarding prior diseases any ongoing treatment and family history of genetic diseases. The complete evaluation includes:-
1. Existing/Emerging illness or disease which may have gone undetected before.
2. Existing risks for the woman who may become pregnant.
3. Existing risks which may affect a fetus if the woman does become pregnant.
4. Depending on the findings women are divided into either
1. low risk group or
2. high risk group
These patients are the advised investigations & medications or nutritional supplements as per requirement.
| Antenatal Care |
|
| Pregnancy is a dream come true of all couples. The first time mothers are filled with apprehension and innumerable questions. |
Basic essential care recommended for all pregnant women |
|
1. |
All pregnant women must have regular Antenatal visits. |
2. |
Blood investigations for Hb, Blood grouping and Rh Typing, VDRL, Blood sugar –R, and a Routine Urine examination with albumin & sugar should be done. |
3. |
Immunization with 2 doses of Td / TT. |
4. |
Iron, Folic Acid and Calcium Supplements. |
5. |
Ultrasound for congenital anomalies should be done before 20 weeks of pregnancy |
6. |
Delivery by a doctor |
7. |
Education on nutrition, diet and hygiene |
8. |
Education in breast feeding and birth spacing and contraception methods |
|
|
Additional care and investigations to be preferably offered |
1. |
Preconception counseling and care |
2. |
Counseling for HIV, HbsAg and HCV testing |
3. |
Counseling and screening for Thallesemia, Down’s syndrome |
4. |
Repeat blood for Hb, Blood sugar screening and Urine methods |
5. |
Evaluation in each trimester |
6. |
Additional screening for infections, growth retardation, thyroid dysfunctions |
Exercise During Pregnancy
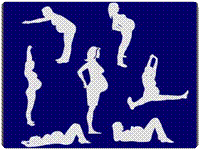 |
Effective exercise during pregnancy can greatly improve the experience of child birth and help speed up the recovery back to your normal weight, post pregnancy.
The intensity of an antenatal workout should be moderate. Exercise intensity should be within recommended guidelines and as the pregnancy progresses certain aspects of the exercise program must be adapted to allow for changes in body shape, size, flexibility and balance.
Those that are not regularly active can still enjoy huge benefit from starting an antenatal exercise program. Even low level exercise can be beneficial in comparison to being sedentary during pregnancy. |
|
Normal Delivery/ Painless Delivery
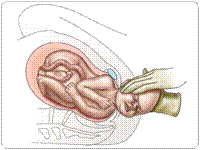 |
| Giving birth is a radical upheaval in human life. It is a process of giving life to new human; Moreover, it is also considered new-life of a lady who just delivered. Children that are born vaginally between the 37th and 39th week are considered as being normal deliveries. Statistically, only 2/3 of all children are born within the 3 weeks around the calculated date of birth and around 80 % within a month around the predicted date of birth. |
|
Giving birth proceeds in three periods: |

|
Dilatation period |

|
Expulsion or press period |

|
After-birth period |
Painless Delivery
 |
At the first delivery-time mothers are filled with apprehension and fear. They get their queries solved by consulting their elders, peers or newsgroups. They develop misconceptions and fears regarding pregnancy and labor.
The perception of pain during labor and delivery varies between individuals. Specially, the first-time mothers need a proper antenatal counselling regarding good nutritious diet, antenatal exercises and physiology of labor pains. |
|
Epidural anaesthesia is an advance in pain management during labor, which ensures that a pregnant woman has a comfortable labor. It is a regional anaesthesia in which an anaesthetic drug is injected near the spinal cord in the spinal canal.
It is administered when the patient is in active labor.
It can be given as a single injection or in multiple doses through a special epidural catheter by a skilled anaesthetist. |
Advantages are |

|
Almost complete relief from pain with the patient being mobile |

|
No post delivery headache as in spinal anaesthesia |

|
Mother is conscious and alert throughout the labor |

|
An instrumental delivery can be performed under the same anaesthesia, if need arises |

|
If the patient has to be taken for caesarean section, the effect can be topped up through the epidural catheter. |
Caesarean Section
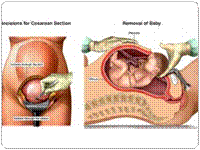 |
A Caesarean section, (also C-section, Caesarian section, Cesarean section, Caesar, etc.) is a surgical procedure in which one or more incisions are made through a mother's abdomen (laparotomy) and uterus (hysterotomy) to deliver one or more babies.
Caesarean section is recommended when vaginal delivery might pose a risk to the mother or baby. In many cases the obstetrician must use discretion to decide whether a Caesarean is necessary. Some indications for Caesarean delivery are: |
|
Neonatal Care
 |
A new born need to be strong enough to withheld stress of the vaginal birth. In the first stages of life numerous processes involving readaptation and adjustment of the organ systems to the extra-uterine conditions take place, especially of breathing, blood circulation and digestive organs. The newborn period cannot be exactly delimited biologically; for purposes of medical statistics, though, it lasts 28 days, divided into an early (1rst week of life) and later neonatal time. The care for the newborn is primarily determined by its vitality and maturity status. |
High risk pregnancy
 |
| GA high risk pregnancy is one in which some condition puts the mother, the developing fetus, or both at higher-than-normal risk for complications during or after the pregnancy and birth. |
Maternal factors include |
|
| |

|
Age (< 15, > 35 yrs) |

|
Weight (pre-pregnancy weight under 100 lb or obesity) |

|
Height (under five feet) |

|
History of complications during previous pregnancies (including stillbirth, fetal loss, preterm delivery, small-for-gestational age baby, large baby, pre-eclampsia or eclampsia) |

|
Five previous pregnancies |

|
Bleeding during the third trimester |

|
Abnormalities of the reproductive tract; uterine fibroids |

|
Hypertension |

|
Rh incompatability |

|
Gestational diabetes |

|
Infections of the vagina and/or cervix; kidney infection; fever |

|
Acute surgical emergency (appendicitis, gallbladder disease, bowel obstruction) |

|
Post-term pregnancy |

|
Pre-existing chronic illness (such as asthma, autoimmune disease, cancer, sickle cell anemia, tuberculosis, herpes, AIDS, heart disease, kidney disease, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, diabetes) |
Fetal factors include |

|
Exposure to infection (especially herpes simplex, viral hepatitis, mumps, rubella, varicella, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, and infections caused by coxsackievirus) |

|
Exposure to damaging medications (especially phenytoin, folic acid antagonists, lithium, streptomycin, tetracycline, thalidomide, and warfarin) |

|
Exposure to addictive substances (cigarette smoking, alcohol intake, and illicit or abused drugs). |

|
Baby has a serious health problem (for example, a heart defect) |
| Furthermore, certain maternal or fetal problems may prompt a physician to deliver a baby early, or to choose a surgical delivery (cesarean section) rather than a vaginal delivery. |
| Top |
|
|
|





